10 Roles of Protein Rich Food: Why Do We Need Protein in Daily Diet?
Protein Helps Improving Muscle Mass
If you want to
- Ligaments
- Tendons
- Body tissues.
A diet lacking protein or amino acids causes
Strength training or such heavy physical activities damage the tissues of muscle for reformation and growing back stronger. Protein helps in not only formation but also in the repair and replacement of these tissues. For an effective process of muscle building, recovery, repair, and replacement for gaining strongness and strength in muscles, extra protein helps significantly. Protein food at this time helps in
Structural Protein Functions: Importance and Uses
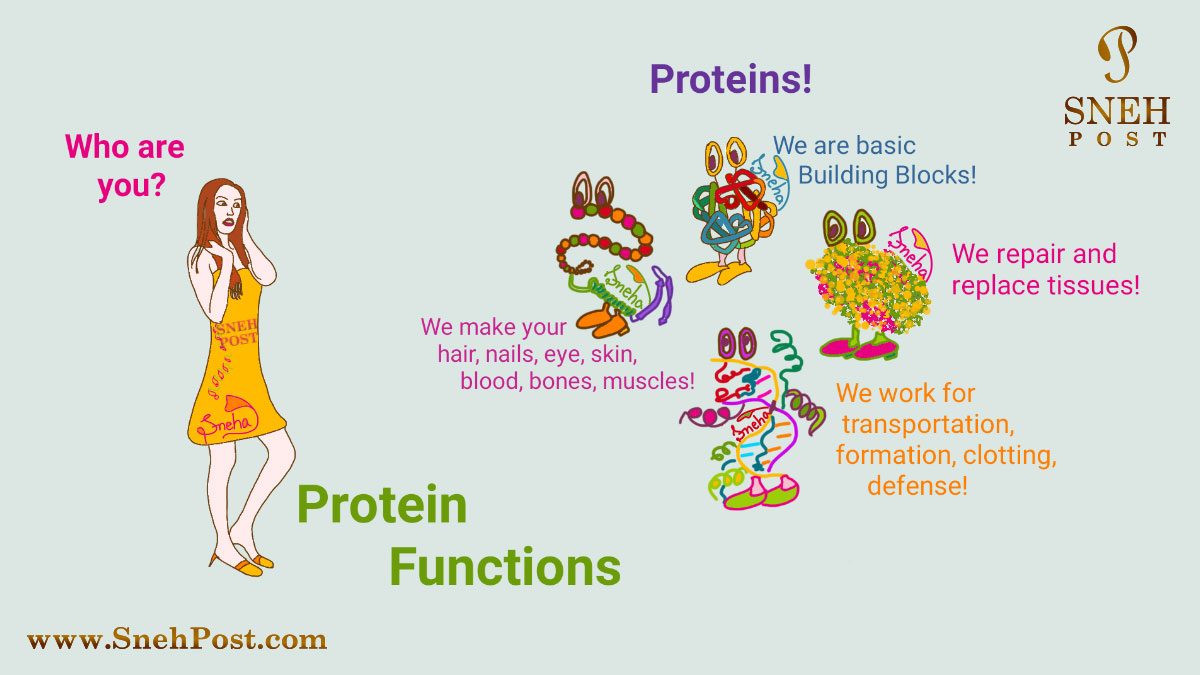
Many of the body parts are made widely from proteins, such as:
- Hair
- Eyes
- Nails
- Bones
- Animal feathers
- Hooves
- Shells.
Protein provides specific structures to body cells, giving skin
Protein is the fundamental building unit that makes:
- Body cells
- Muscles
- Arteries
- Bones
- Veins.
Proteins help to
Protein Benefits: 10 Unthanked Uses
Protein For Child Growth: Why It Is An Overrated Nutrient?
Strengthen the Body Parts
These fibrous ones strengthen some of the body parts such as:
- Hair
- Horns
- Beaks
- Feathers
- Quills.
Protein Maintains Blood Sugar Level
Proteins affect the
In our daily life, about 50g of protein is required to
This suggests that as half of the protein intake consumes in compensating the daily protein loss, we get only half of the protein amount to use as
So it can be said that protein can affect the blood sugar level by just half of the carbohydrates.
This theory is the basis of supporting
However, there are no sure shreds of evidence available to prove that the low carbohydrate diets which are high in proteins are helpful in the long-term too. The evidence talks about this diet’s immediate or initial effects only, which means such diet helps in weight loss at the beginning of the journey, but how this philosophy works in long terms, no research states about this.
The study shows that protein affects much lesser, almost neutral effects on blood sugar levels in comparison to carbohydrates, and even fats. Protein does not cause a rise in blood sugar level, if consumed alone, keeping it steady.
Proteins Save from Mood Swings
Some amino acids that contribute to making protein structures help to balance hormones, controlling anxiety, and mood swings as a natural remedy. Protein not only helps in maintaining a
Proteins keep the following problems at bay:
- Weakness
- Anxiety
- Moodiness
- Unstable glucose level
- Mood changes
- Cravings
- Irritation
- Fluctuating blood sugar levels.
Protein Helps in Weight Management
Protein can be a splendid hero for any
Many people follow a weight loss strategy in which they intake controlled calories with additionally added high protein foods. This helps to lose weight practically. Know below how!
Refined or sugary carbohydrate sourced like fried food items and sweets easily tempt anyone and play villain ruining your diet and weight goals. But you feel satiated and satisfied after taking protein and stop craving food.
When a low-calorie diet leads you towards muscle loss, protein wards and proves itself as a superhero for weight loss.
Protein for Energy: 3 Unsaid Usage
Protein Supports Brain Functions and Learning Capabilities
Amino acids play a vital role in learning and cognitive functions through contributing to processes and formation of:
- Hormones
- Enzymes
- Neurotransmitters.
Proteins support
High Protein Benefits in Heart Health
Protein-rich food intake decreases the risk of
Protein as Antibodies: Protect Your Body from Viruses & Bacteria
Antibodies are proteins that protect our body by binding with foreign invaders or antigens such as
Contributes to Make Strong Bones
The most important role that protein plays, is increasing the integrity of the system, organs, and bones at all your life stages and age. Too much protein affects too low in comparison to deficiency of protein in the diet and thus the body.
Low protein results in
The studies on the relationship between protein and bone health show contradictory results. So to understand the facts, you need to understand their chemistry deeper to know whether the protein is beneficial or harmful for bones.
Some studies say that high proteins cause the body to lose calcium and this calcium excretion adversely affects the bones. Other studies say that proteins increase the
- Heal broken bones
- Prevent fractures
- Helps in bone weakness
- Prevent Osteoporosis.
This way, the advantages of protein-rich food offset the loss of calcium.
Protein Promotes Slow Aging, Leading You towards Longevity
Protein plays a vital role in synthesizing the master antioxidant- glutathione. This antioxidant glutathione remains stored in our cells and helps to detox. It also reduces carcinogens that cause
Avoiding protein can become a reason for glutathione deficiency and lead to oxidative stress. Avoiding protein in the long term can cause age-related diseases and disorders such as
What shows that we are aging is mainly our body and muscles which appear like decaying due to tissue loss. A balanced diet that incorporates protein in a sufficient amount fulfills the need for amino acids, preventing muscle loss by keeping muscles intact. It also maintains immune functions, high cognitive mechanisms, and supports strong bones.
As we age, the capability of our body to synthesize amino acids decreases so the importance of eating plenty of protein resources mounts to keep the balance, strength, body weight, memory, and energy level in place.
Role of Protein Hormone in Signaling
The glands in various parts of our body produce hormones that are basically chemicals. Some hormones are made or produced using combinations of some amino acids, which are classified as protein hormones. Our pituitary gland produces growth hormone and the pancreas produces insulin. They come under the category of protein hormones. These hormones are important to our body and the lack of protein or other related affecting factors can make us lead to serious medical conditions, such as it can cause one to face growth disorder or disease like diabetes.
The endocrine system remains connected to the glands and body organs producing hormones. They maintain a network between them. This communication controls various parts of our body. Protein hormones transfer the signals between the cells of the endocrine system and other parts of our body. Their cellular signaling activity and ability to induce metabolic reactions make them important as they can increase or decrease them. For example, they can affect the protein synthesis mechanism.
Speed-up Your Body Reactions with Protein (Enzymes) Rich Diet
Although most enzymes are proteins, yet all the enzymes are not protein-based such as ribozymes. Enzymes or biologically active molecules of proteins possess a small amount in our body and are produced by our organisms.
These are active catalysts that participate in the chemical reactions of our bodies. They are not consumed, destroyed, or transformed during the reactions, and they also cannot make a reaction happen, but they catalyze or speed up the biochemical activities of the cells. They affect mechanisms such as:
- The reaction of cellular communication
- Energy production
- Clotting of blood, etc.
Such two enzymes are pepsin and lactase. Pepsin reacts in the stomach as a
Protein enzymes are important for thousands of biochemical reactions that happen in our body cells. Enzymes lower down the activation energy of any reaction and make them happen a
Thus proteins of cell membranes contribute to various enzymatic activities.
Membrane Protein as Supporter Element for Cellular Membranes
Those proteins which reside in the plasma membrane helps to build cells' interaction with the surrounding environment. They carry out some diverse, vital functions like receiving signals of chemicals from outside of cells, transporting nutrients across the membrane, translation of chemical signals into for executing the intracellular actions, and cell anchoring in varying body locations.
Proteins like glycoproteins are an important element of
Membranes are thin sheet-like structures that act as a partition, lining, boundary, or surface for any organ. Proteins are found on these membranes’ surfaces or both sides or buried inside in any portion of it called domain.
Proteins that get extracellular domains that exist outside the cells behave communicators who involve in the cell-to-cell interaction. Mainly proteins reside inside the membrane and help to form the channels making pores for molecules that are surpassed to cross the membrane.
Proteins that get cytosolic domains (existing inside the membrane) involve a wide range of functions. They take part in intracellular signaling activities.
Protein Supports Blood Functions
Proteins not only contribute to the formation of blood cells but also help these blood cells in many functions like:
- Transportation of oxygen
- Balancing pH
- Defense
- Distribution of water
- Clotting.
Protein usages in
Blood Protein: 5 Unsaid Roles of Hidden Proteins
You may also like:
How Much Protein I Need Per Day at 15 Different Ages, Conditions
Nutrients: Vastly Knowledgeable Nutrition Guide
Best Malnutrition Guide: 'No' to Nutritional Imbalance