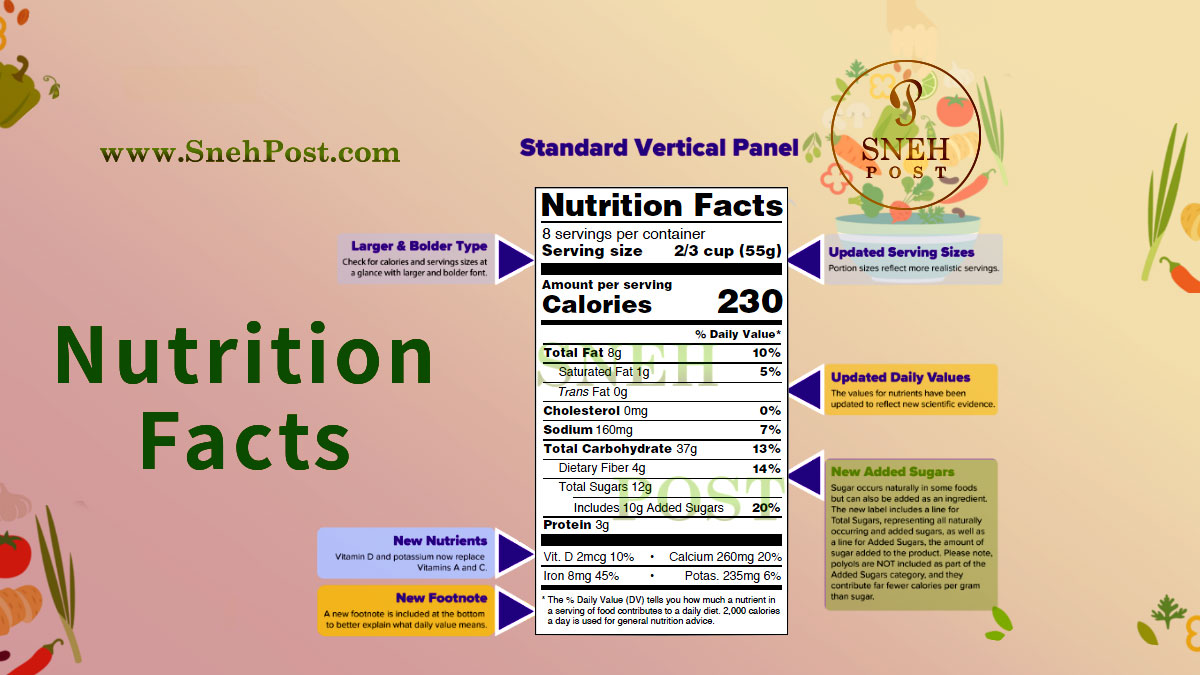
Nutrition Facts Label or Nutritional Value or Food Label

These food labels are marked as the nutrition guide on any food product or food package, which provides information about what nutrients and how many calories that particular food contains. In addition, this nutrition facts label also contains the information about how much energy can be provided to how many people through that product or package; while the details are mentioned considering 2,000 calorie plan (This plan recommends 2,000 calories per day to humans for living healthy).
Such information shows whether the food that you are going to eat is healthy and balanced or not. If one follows the nutrition-related information keeping an eye on calories and nutrients, one can avoid many diseases and disorders because of
 Best Malnutrition Guide: 'No' to Nutritional Imbalance
Best Malnutrition Guide: 'No' to Nutritional Imbalance
The Terminology of Nutrition Facts Label Listing in Food Lebel
For understanding the food label and marked nutrition facts (nutrition value or nutrition guide), one needs to understand the terminology that is used on any food package or food product.
Number of Servings
"Number of servings" in a food label refers to the number of people that can consume that particular amount of food.
For example:
- 2 servings
- 8 servings
Usually, the number of servings is mentioned at the top of the Nutrition facts label list.
Serving Size
The serving size on any food label refers to the amount that is consumed by a person at one time. This mention in any nutrition facts label list is the quantity of food or drink which is suitable to serve one person, considering nutrition and weight control.
Serving size is the standardized quantity of food or drinks to give you an idea about its
 Nutrition Science Wonders: Meaning and Basics
Nutrition Science Wonders: Meaning and Basics
For Example
Below are some examples for serving size formats in a Food Label:
- One small/medium/ large-sized fruit (such as banana, apple, orange, pears)
- 3/4 cup of 100% fruits or vegetable juice
- 1/2 cup of raw/ cooked/ frozen/ canned/ cut-up fruits
- 1/2 cup of raw/ cooked/ frozen/ canned vegetables
- 1/2 cup of cooked/canned legumes (such as peas, beans)
- 1 cup of raw/cooked/leafy vegetables (such as spinach, lettuce)
- 1/4 cup of dried fruits such as mangoes, apricots, raisins)
Measurement of Serving Size in Nutrition Information Panel
The sizes of most of the products are measured in common units. Take a look at some examples of serving sizes formats that are usually used in the nutrition facts label list of the food product.
Examples:
- For sugar, the serving size is giving in tablespoon or cup
- For the cake, the serving size is given fractions, such as 1/8 cake, which means the whole unit of one cake has 8 portions. Either the 8 portions of this one cake can be served to 8 people or one person can eat the 8 portions at 8 different times, one-by-one.
- For olives, the reference amount is seen. If the total amount is 40g and one olive’s weight is 10g, then the serving size might be listed as four olives on a nutrition facts label.
Portion Size
Portion or Portion Size is also a term that is used to refer to the amount of food served to one person. This term is popular in restaurants, cafes, or shops that sell ready-to-eat food items or packages. Though again, one can find the distinction as food manufacturers or chefs of any restaurant might take a self-selected portion size.
What portion size is adequate for a person also depends on:
- Palatability of a food
- The capacity of that food to reduce one’s hunger
- The ability to generate fullness
- Providing expected satiety
If we go on the basics, portion size cannot be seen as a part of the nutrition facts label as it depends on the various aspects (as mentioned right above).
Difference between Serving Size in Food Label and Portion Size
Where serving or serving size terms are mentioned in Nutrition Information Panel for the food amount recommended by consumer education materials for nutrition facts label, 'portion' or 'portion size' terms are referred to the food amount that you select for one time which might be more or less than the serving size. So on standard food packages, serving size is a more popular term for mentioning in a nutrition facts label.
For Example:
- 1 teaspoon of sugar can be seen as the size of a dice
- 1/2 cup of fruit can be seen as the size of a tennis ball
- 1 cup of the vegetable can be seen as the size of a basketball
- 1 ½ ounce of butter can be seen as the size of four stacked dice
- 3 ounces of meat can be seen as the size of a deck of cards
The serving size on a food label is mentioned to compare your portion size and listed portion size on any nutrition facts label or nutrition information panel. A person can know how many calories he is taking.
A good trick to overcome portion distortion is:
Prefer to eat on a plate, not from a package. This will help to take an idea of how much you are eating.
Eat food in the smaller dishes so that the less will look more. Try to eat at the lunch plate.
Once you get an idea and sense of the difference between serving and portion size, you will be able to compare and make the required modifications.
Energy
The energy value on any food label or nutrition information panel refers to the total amount of kilojoules (abbreviated as kJ) from Carbohydrates, Proteins, dietary fiber, alcohol, and Fat that will release when the body will use the food.
The listed lower energy in a nutrition facts panel usually refers to a food that is low in sugar and fat. Such choices are comparatively better for most people.
Difference between Kilocalories (Kcal) and Kilojoules (kJ)
Some nutrition facts label confuses about energy amount as some show the energy in kilo-joule instead of Kilo-calorie. Check out below the measurements for convenience!
1 Kilocalorie = 4.184 Kilo-joule
(Where,
Kilocalories = 1000 Calories
1 Kilo joule= 1000 Joule)
Total Calories
Total calories listed in the nutrition facts label gives information about calories in a single serving. It helps weight watchers who want to gain weight or plan for a weight loss.
Percent Daily Value (% DV)
Percent daily value in nutrition facts label list can be your ultimate guide for helping you in the evaluation of food. You can get an idea through the percentage daily values of the food label, for knowing whether your food fits into your daily diet plan or not.
Percent daily values refer to the average levels of nutrients for people following 2,000 calories per day plan. % DV on a nutrition information panel shows that a food item has how much percentage of a nutrient for fulfilling the demand of that particular nutrient to reach your 2,000 calories goal.
For example:If a Nutrition facts label says that the food contains 10% DV (10 percent daily value) of fat, it means a person planning to intake 2,000 calories will intake 10% of the total fat by eating that food.
This % DV in the list of Food Label is mentioned for the entire day, and not for just that one snack or meal.
How much percentage of a nutrient is needed might differ from person to person. In some personalized cases, one might need more or less percentage of a nutrient, which means 100% daily value might be less or more of what is listed in the nutrition facts label.
High Percent of Daily Value in Nutrition Information Panel
20% or more is considered high. A person is recommended to aim at a diet that is high in vitamins, fiber, and minerals.
Low Percent of Daily Value in Food Label
5% or less is considered low. A person is recommended to aim diet that is low in cholesterol, trans fats, saturated fat, and sodium.
What to Limit
The nutrition information panel not only lists the content of a food packet but also helps in following a healthy diet plan. Check out the fat, cholesterol, sugar, and sodium content in the food label list and if the nutrition information panel suggests a higher amount of these, then limit the food consumption as per your health state.
Good Fat Vs Bad Fat Foods: What to Eat and What to Avoid?
- Eat food that is low in trans fat, saturated fat, sodium, and added sugar. Limiting these reduce the risk of chronic diseases. One should try to eat a low percentage daily value of these nutrients. Nutrition facts label helps you in limiting the food that goes oddly to your diet plan.
- Trans fat and saturated fats increase the risk of heart-related problems. One should avoid the consumption of trans-fat-rich foods.
- Added sugar makes it tough to fulfill the requirement of nutrients within your diet plan. A high amount of sodium can result in high blood pressure. So watch the quantity!
- One should try to introduce a low percentage daily value of these nutrients in the diet.
What to Add More?
Take a glance at the food label for fiber and vitamins rich foods as they are usually a healthy option for all health states. Take the help of a nutrition information panel to ensure you eat them in a sufficient amount.
- Intake a diet that is rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Check nutrition facts label to get an alarm about limiting nutrients that should be consumed lesser for good health.
- Fiber, vitamin D, calcium, potassium, and iron help in reducing the risk of health issues such as anemia and osteoporosis. Ensure the presence of such elements in your food plate.
- Introduce fruits and vegetables to your daily diet to meet the requirement of these good nutrients.
- One should aim to include a high percentage daily value of these nutrients in the diet.
Additional Important Nutrients
Only knowing about calories from a nutrition information panel is not enough. You also need to have knowledge about additional nutrients mentioned in the list of nutrition facts label, which are:
Carbohydrates
If you need energy, check the food labels for carbs content. Carbohydrates are the prime source of energy. Carbs are found in three forms: sugar, fiber, and starch. Eat whole-grain, rice, cereals, and bread with fruits and vegetables to refuel your body.
Carbohydrates: List of 3 Types of Energy Givers
Sugar
Our food naturally contains sugar, that is, simple carbohydrates. Some food items such as fruit juice, milk, table sugar, and corn syrup are amazing natural sources. It is recommended to avoid more than 10 percent of daily calories from added (additional) sugar.
Protein
Protein Guide: 5 Finest Writings Collected
Usually, a percentage daily value of protein in the Nutrition facts label is mentioned as per it is not worth considering or required to give attention. A person can eat moderate portions of protein-rich food sources, such as lean meat, eggs, low-fat milk, fish, cheese, yogurt, poultry, soy products, peas, beans, seeds, peanut butter, etc.
How Much Protein I Need Per Day at 15 Different Ages, Conditions
This section in food labels is worth focusing on those who are on a weight loss or weight gain journey. People who are on a body-building mission, they also need to watch their protein intake amount.
Protein Function: 15 Wonderworks of Protein in Body
Protein for Energy: 3 Unsaid Usage
Calories from Fat
Calories from fat in a Nutrition information panel refer to the calories in a product, which you will get directly from fat after eating the food.
It is recommended to intake less than 10% of calories from saturated fats. Trans fats are considered bad fats, so one should try to keep their amount as little as possible in the food.
Essential Fatty Acids: Needful yet Underrated Nutrition
Nutrition Label List Content: 15 Core Nutrients
Usually, the following 15 contents are mentioned in a nutrition facts list so that you can take an idea about the nutritional value of that food:
Calories, fat, trans fat, saturated fat, calories from fat, cholesterol, carbohydrate, sugars, dietary fiber, protein, vitamin A, vitamin C, sodium, iron, and calcium.
Ingredient List
The nutrition facts label also includes an ingredient list if more than one ingredient is used in the recipe. The ingredients are arranged in descending order of their weights, which means the larger weight-containing ingredient will be listed first, and the smaller in last. This list of food label contents is helpful for those who are pure vegetarian or do not want to intake shellfish or pork. It is a useful piece of information for those too who are aiming to cut the added sugars.
Nutritional Claims or Nutritional Content Claims
A nutrition information panel not only includes information about total sugar, sodium, fatty acids, and other nutrients but also mentions the nutrition claims.
Nutritional content claims give information about nutrients and substances, such as a good source of calcium, high in vitamin A, low in fat, a good source of fiber, etc.
Health Claims
Health claims in a nutrition facts label are not just statements about the content of any food, but it is more than just a piece of information. It informs about the relationship between health and food.
Health Claims can be divided into two as per their level of intensity.
Health Claims of General Level
These health claims give information about the effects of food on health, such as calcium for strong bones and healthy teeth. This level of health claims does not talk about serious health problems or diseases.
Health Claims of High Level
This type of health claim refers to the relationship between food and serious disease, such as Phytosterols may decrease the level of blood cholesterol, high calcium diet may reduce osteoporosis risk in 65 years or above this age of people.
Cautions and Patient Warnings
Apart from nutritional claims, food labels show warnings, cautions, or patient warnings too. The nutrition facts label indicates cholesterol, artificial sweeteners, sugar levels, and allergens.
Significance of Nutrition Facts Label
Healthy Diet Chart: 9 Zappy Eating Times

 List of Nutrients: 7 Types and Whopping Food Sources
List of Nutrients: 7 Types and Whopping Food Sources